
What Are Migraines?
Migraines are more than just bad headaches. Read on to learn more about migraine headaches, symptoms, and various treatment options.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Migraine Headaches
Migraine headaches impact the lives of millions of people around the world. Data from the Migraine Research Foundation suggests that more than 39 million Americans live with chronic migraine headaches.1
Those who live with migraines experience significant and detrimental effects on their overall health and well-being. In some cases, migraine headaches are brief. However, for others, they can last for hours or even days.
Everything from family and employment obligations to essential self-care and family relationships are affected for these individuals.
Note About Migraines
Doctors and researchers believe that the true number of people with migraine headaches in the United States and worldwide is far higher. This is because many people who live with migraines do not seek medical help, and therefore, their cases go unreported.
What Are Migraine Headaches?
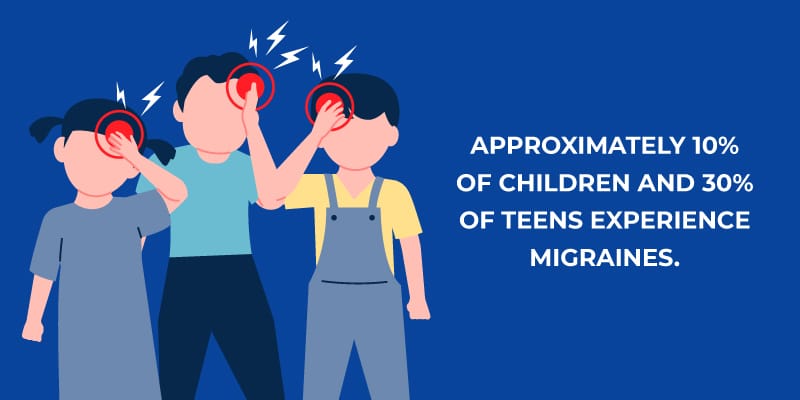
Migraine headaches are a neurological disease resulting in a throbbing, pulsing headache on one side of the head.2 They can be a debilitating condition that sometimes leaves sufferers bedridden for days. Migraines can affect people at all stages of life, including children and teenagers.
Also, migraines may present differently in children than in adults. For example, before puberty, migraine headaches are more common in boys, but after puberty, girls are more likely to experience more frequent and more severe migraine episodes.
How Do Children Develop Migraines?
The same study also indicates children are 50% more likely to develop migraine headaches if one parent has them. This increases to 75% if both parents are affected.

Are There Different Types of Migraine Headaches?
There are two basic types of migraine headaches. Episodic migraines are defined as experiencing migraine symptoms fewer than 15 days per month.
Conversely, chronic migraine headaches occur more than 15 days per month for three or more consecutive months. It is common for migraine sufferers to progress from episodic migraine headaches to chronic migraines over time
How Do These Occur?
In some instances, this progression has been associated with overusing certain medications to control headache pain, such as barbiturates, opioids, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They may also be attributed to excessive consumption of caffeinated beverages.
Other medical conditions that may be associated with the development of chronic migraine include sleep apnea, anxiety, depression, and obesity.4
What Is Migraine Aura?
A migraine aura can happen either before a migraine occurs or with the migraine. Typically, it presents with visual symptoms but can also cause other disturbances.
Migraine aura usually begins approximately one hour before other migraine symptoms and may serve as a “warning” of an impending migraine headache.
Learn More About Migraine Auras
Migraines vs. Headaches
Migraines are not just bad headaches. Several differences separate a migraine from a headache, including additional, debilitating symptoms.
The causes of migraines and headaches are also distinctly different. Although both issues can include head pain, migraines are a neurological disease that can cause further symptoms such as nausea, fatigue, and increased sensitivity.
Types of Headaches
- Tension-type: As one of the most common types of headaches, tension headaches are often caused by factors such as poor sleep, stress, muscle strain, and anxiety. It typically presents as pain behind the eyes and in the back and neck.
- Cluster headaches: These painful headaches tend to occur in clusters. They may last for a few days or a few months, with a month or more of pain-free periods. These headaches are triggered by the dilation of blood vessels that pressure the trigeminal nerve. Some experts also believe irregularities in the hypothalamus might cause it.
- Hemicrania: This type is a one-sided, daily headache without a cause. Other symptoms can include nausea, sensitivity to light, watery eyes, and congestion.
One characteristic that sets migraine headaches apart from other types of headaches is that migraines are more than a “type” of headache. Migraine headaches are a primary disorder where a headache is one of many symptoms.
Migraines: More Than Just a Headache
Migraine Risk Factors
- Hormonal changes in women, such as pregnancy, menopause, or around menstrual periods
- Drinks, especially coffee and alcohol
- Stress, either work or personal
- Weather changes or barometric pressure, such as being in an airplane
- Foods, such as processed foods and aged cheeses, as well as skipping meals
- Food additives, such as MSG and aspartame, found in many processed foods
- Getting either too much or too little sleep
- Medications, including oral contraceptives and vasodilators
- Sensory stimuli, such as bright or flashing lights, strong smells, or loud noises
- Physical factors, such as intense exercise
Migraine Causes
Although the causes of migraines are not completely understood, experts believe that both genetics and environmental causes play a role in the development of migraines. Some key risk factors for migraines include:
Age
Typically, migraine symptoms start during adolescence and continue in intensity until your 30s. From there, they begin to reduce in severity and frequency.
Sex
Family History
Brain Chemistry and Structure
Another potential contributing factor to migraine headaches is brain structure and the release of neurotransmitters.
Researchers believe that changes in the brainstem itself and how it interacts with the trigeminal nerve. Imbalances of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which helps to control pain, may also play a role.

Common Symptoms of Migraine
Migraine symptoms typically occur in four phases: prodrome, aura, attack, and postdrome. Each stage has its own distinctive set of symptoms that a person suffering from migraine headaches may experience.
It is important to remember that not everyone who has migraine headaches will experience all four stages with each episode.
Prodrome Symptoms
- Food cravings
- Mood changes ranging from euphoria to depression
- Neck stiffness
- Increased urination
- Frequent yawning
- Fluid retention
- Constipation
Migraine Aura Symptoms
A migraine aura can happen before or during a migraine headache. Typically, symptoms occur gradually and build over several minutes.
As noted above, auras usually consist of visual symptoms. However, other disturbances can also occur. Symptoms of a migraine aura can last as long as an hour before dissipating and may include:
- Visual phenomena
- Pins and needles sensations
- Difficulty speaking
- Numbness or weakness
- Temporary loss of vision
Migraine Attack Symptoms
A migraine attack can last anywhere from four to seventy-two hours. These attacks vary from person to person. Some people might rarely experience them, while others have them several times a month.
Symptoms of a migraine include:
- Pain on one or both sides of the head
- Sensitivity to sounds, light, and even touch and smell
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain that throbs or pulses
Postdrome Symptoms
After the migraine, many are confused, washed out, or drained. Others report that they feel exhilarated once the attack passes. However, sudden movements can briefly bring back the migraine pain.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Migraine Headaches?
If you have a family history of migraine headaches or experience them, it is important to schedule an appointment with a neurologist. They can conduct an evaluation and assess factors that could contribute to your headaches, such as family history and current symptoms.
They will also perform a physical and neurological exam to help determine if there are other potential causes of your headaches. Depending on the nature and severity of your symptoms, your neurologist may suggest other, more in-depth tests such as:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan
CT scans are comprised of a series of X-rays. They form a detailed cross-sectional picture of the brain when put together. Like an MRI, this can help diagnose or rule out other medical conditions that could cause headaches.
Types of Treatment for Migraine Headaches
Science and medicine have innovated new migraine treatments to provide hope for those with migraine headaches.
Home Remedies
There are lifestyle changes that can help prevent and soothe migraine symptoms. Laying down in a dark and quiet room and placing a cool cloth or ice pack wrapped in a towel on your head can help bring some relief. Drinking a lot of water and staying hydrated can also help with migraine symptoms.
Stress can cause migraines, so relaxation techniques can also provide powerful support. If you experience migraines, consider activities such as meditation or finding a hobby you enjoy.
Regular, moderate exercise can also reduce tension and maintain a healthy weight to help prevent migraines. With your doctor’s approval, swimming, cycling, and walking with a slow warm-up period are exercises to consider.
Other Home Remedy Options
Regular sleeping and eating routines are also a way to prevent severe migraine headaches. Avoid over-or under-sleeping, and following set times to sleep and wake up can help. Additionally, regular meals at the same time each day can help prevent sudden blood sugar fluctuations that can contribute to migraines.
Biofeedback
Stress can be a risk for those who frequently experience severe migraines. Biofeedback is a form of neurotherapy that can be a powerful tool for relaxation training.
A session involves using equipment to monitor body functions while a practitioner offers strategies to change how your body functions.
Acute Treatments
Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers can bring temporary relief for migraines. However, taking medication for too long can have serious side effects, including headaches caused by medication overuse, ulcers, and gastrointestinal tract bleeds.
The prescription drug Triptan can help block pain pathways in the brain as a migraine treatment. Some other migraine treatment medications that can bring immediate relief include dihydroergotamine and Lasmiditan.
Anti-nausea medication, such as Reglan and Compro, can also help relieve the gastrointestinal symptoms that sometimes accompany severe migraines.
Preventative Treatment
While not always possible, avoiding risks is a powerful way to prevent migraine headaches from occurring. Medication can also help treat chronic migraines.
Some medicines that a doctor might prescribe to prevent severe migraines include:
- Antidepressants
- Blood-pressure lowering medications
- Botox
- Anti-seizure drugs
- CGRP monoclonal antibodies

How J. Flowers Health Institute Can Help You Heal From Migraine Headaches
If you are experiencing migraines, consult a health practitioner from J. Flowers Health Institute for help finding treatment.
Although it is not always possible to entirely prevent migraine headaches, there are many tools available to reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines on your health and well-being.
How Can We Help?
If you are experiencing pain from migraine headaches or have developed migraines as a symptom of another disorder, we are here to help. Our Living MRI offers comprehensive diagnostic tools to help determine the root of your symptoms.
Then, we can work with you to create a personalized treatment plan that will support you every step of the way during the healing process.
Reach Out to Us Today
Contact us today to learn more about how J. Flowers Health Institute can help with migraine treatment and management. Getting the help and treatment you deserve can make all the difference for getting you back to living a life free of migraine pain.
Resources
- https://www.singlecare.com/blog/news/migraine-statistics/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/symptoms-causes/syc-20360201
- https://migraine.com/migraine-statistics
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2787727#:~:text=Migraine%20affects%20an%20estimated%20more,Are%20Episodic%20and%20Chronic%20Migraine%3F
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/symptoms-causes/syc-20360201
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/headache-disorders
- https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/health-and-wellness/2019/november/migraines-vs-headaches
- https://www.healthline.com/health/migraine/triggers
- https://headachejournal.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01900.x
- https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/migraine/#inheritance
- hhttps://www.webmd.com/migraines-headaches/understanding-migraine-symptoms
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20360207
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2787727#:~:text=Migraine%20affects%20an%20estimated%20more,Are%20Episodic%20and%20Chronic%20Migraine%3F










