
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
At J. Flowers Health Institute, we understand how carpal tunnel syndrome can negatively impact your quality of life. We’re here to help.
Table of Contents
Art Therapy
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
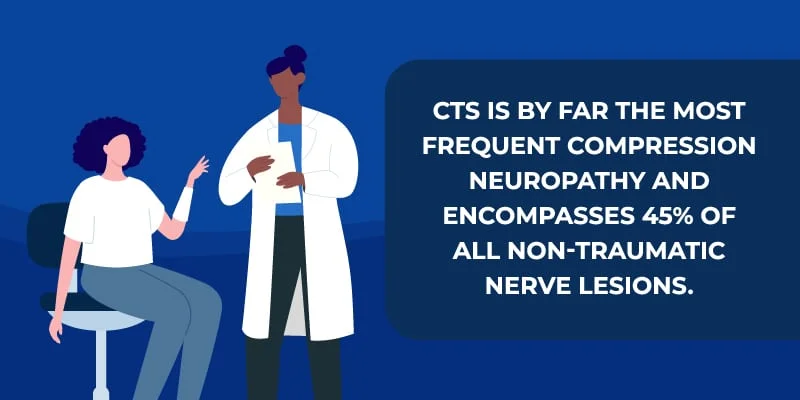
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common condition affecting millions worldwide. It is a medical condition that affects the hand and wrist.

When Was CTS First Identified?
A Closer Look at Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Who is Most Likely to Develop Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Share This Article
Categories
Top Blogs
Recent Post
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
There are many contributing factors that can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome. Some of these factors are detailed below.3
Repetitive Hand and Wrist Movements
- Using vibrating tools
- Assembling things
- Typing on a keyboard for extended periods
- Playing musical instruments
- Engaging in certain sports
Continuous use of the hands and wrists can lead to swelling and inflammation in the carpal tunnel. The increased pressure within the confined space compresses the median nerve, resulting in the characteristic symptoms of CTS.
Contributing Factors
Genetics
Underlying Health Conditions
- Inflammation
- Fluid retention
- Tissue changes contributing to nerve compression
Pregnancy
Obesity
Wrist Injuries
Inflammatory Conditions
Risk Factors for Developing CTS
Occupations With High CTS Risk
- Computer-related work: Typing on keyboards and using computer mice for extended periods.
- Manufacturing and assembly line work: Repeatedly using vibrating tools or performing fine motor tasks.
- Cashiers and supermarket workers: Constantly scanning items and handling products.
- Musicians: Playing instruments that require repetitive hand and finger movements.
- Hairdressers: Frequent use of scissors and hair dryers.
- Construction workers: Using vibrating power tools and performing repetitive motions.
What is CTS? Causes and Overview
Gender and Age-Related Predispositions
Common Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Numbness and Tingling in the Hand and Fingers
- Thumb
- Index finger
- Middle finger
- Part of the ring finger
Pain and Discomfort in the Wrist and Forearm
Patients with CTS often experience pain and discomfort in the wrist and forearm. The pain may be dull, aching, or sharp and can vary in intensity.
It’s often felt in the palm and the thumb side of the hand, and it may radiate up the forearm. The pain is often more pronounced at night or upon waking up.
Weakness and Difficulty Gripping Objects
Recognizing the Progression of Symptoms
- Stage 1: This is the earliest stage of CTS. The symptoms are mild and may come and go.
- Stage 2: The symptoms become more constant and may interfere with daily activities.
- Stage 3: The symptoms are severe and may cause permanent damage to the nerve.

Differentiating CTS from Other Hand/Wrist Conditions
Several hand and wrist conditions can present symptoms similar to carpal tunnel syndrome. It’s essential to differentiate CTS from other conditions to ensure appropriate treatment.
Some conditions that may mimic CTS symptoms include:
De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
Arthritis
Arthritis can affect any joint in the body, including the joints in the hand and wrist. Symptoms of arthritis include:
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Decreased range of motion
Types of Arthritis
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is inflammation of a tendon, a band of tissue connecting muscle to bone. Tendonitis can occur in any tendon in the hand or wrist, but it is most common in the tendons that move the thumb and fingers.
Symptoms of tendonitis include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness in the affected area
Neuropathy
- Diabetes
- Alcohol abuse
- Certain medications used in chemotherapy
Differentiating Neuropathy from CTS
Cervical Radiculopathy
Compression of nerves in the neck (cervical spine) can cause symptoms that radiate down the arm, mimicking CTS. It can be difficult to differentiate between the two because of the mimicking symptoms.
Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Medical History
The diagnosis of CTS begins with a comprehensive medical history conducted by a healthcare professional.
During the medical history, the doctor will ask about the patient’s:
- Symptoms
- Frequency
- Any factors that aggravate or reduce them
Physical Examination
The healthcare professional will assess the patient’s hand, wrist, and forearm in the physical examination.
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Muscle wasting in the hand
Our team will perform specific tests to evaluate the function and sensation of the median nerve. Some common physical tests that we may utilize at J. Flowers Health Institute include:
Tinel’s Sign
Wrist Flexion Test (or Phalen Test)
Electrodiagnostic Tests
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
Electromyography (EMG)
Imaging Techniques
Ultrasound
MRI
X-Rays
Prevention of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Take Breaks
Avoid Repetitive Movements
Use Proper Ergonomics
Strengthen Your Hands and Wrists
- Shaking your hands
- Opening and closing your fist in controlled movements
- Touching each fingertip to your thumb tips
- Squeezing a soft rubber ball for a few seconds
Lose Weight
Quit Smoking
Additional Tips
Use a Wrist Splint: A wrist splint can help to keep your wrist in a neutral position and reduce the pressure on the median nerve.
Massage Your Hands and Wrists: Massage can help to improve circulation and reduce muscle tension in your hands and wrists.
Keep Your Hands Warm: Cold temperatures can constrict blood vessels and increase the risk of CTS. Keep your hands warm by wearing gloves or using a heating pad.
Drink Plenty of Fluids: Staying hydrated can help to reduce inflammation and improve circulation.
Get Enough Sleep: Sleep is essential for your health and well-being. Getting enough sleep can help to reduce stress and improve circulation.
Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Non-Surgical Interventions:
Rest and Activity Modification
Wrist Splints and Braces
Physical Therapy
- Wrist flexibility
- Strength
- Range of motion
Medications for Pain and Inflammation
7 Easy CTS At-Home Remedies
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be considered if non-surgical interventions do not effectively reduce symptoms or if the condition is severe with significant nerve compression.
Indications for surgery include:
- Persistent or worsening symptoms
- Weakness in the hand grip
- Evidence of nerve damage confirmed through electrodiagnostic tests
Open Release Surgery
Endoscopic Release Surgery
Post-Surgery Recovery and Rehabilitation
Living with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Living with chronic CTS can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, mental health, and well-being. Proper management and early intervention are crucial to minimizing these effects.
Coping Strategies
- Avoiding activities that worsen symptoms
- Using assistive devices for certain tasks
- Applying cold packs to reduce inflammation
Modifying Daily Tasks
- Using ergonomic tools and equipment
- Alternating between hands for tasks
- Incorporating regular breaks
Support Groups

Get the Treatment You Need at J. Flower Health Institute
Our team of experienced health practitioners is dedicated to providing you with the best possible care. We use the latest diagnostic tools to ensure we make the correct diagnosis, even when symptoms mimic other hand conditions.
What We Provide and How We Can Help
- Physical examinations
- Medical evaluation
- Chronic pain evaluation
- Lifestyle assessment
- Comprehensive report and action plan
Reach Out and Begin Healing
If you are experiencing symptoms of CTS, don’t wait. Call J. Flower Health Institute today to schedule an appointment. We will work with you to find the right treatment for you.
Resources
- https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/carpal-tunnel-syndrome#:~:text=Carpal%20tunnel%20syndrome%20(CTS)%20is,may%20become%20swollen%20and%20useless
- https://bmcmusculoskeletdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12891-015-0685-0
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/carpal-tunnel-syndrome-causes-risk-factors-2549308#citation-6
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/de-quervain-tenosynovitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20371332
- https://www.healthline.com/health/arthritis-wrist#treatment
- https://www.jospt.org/doi/pdf/10.2519/jospt.2004.34.10.565









