

What Is Spinal Stenosis
Discover everything you need to know about spinal stenosis and how to treat the condition here.
Table of Contents
What Does Spinal Stenosis Feel Like?
Spinal stenosis is a condition caused by the narrowing of the spine, specifically affecting the spaces within the spine and putting pressure on the nerves. This can lead to chronic pain in the back and neck, and if left untreated, can significantly reduce quality of life.
Although spinal stenosis is characterized by pain in the back and neck, in some cases, it can radiate throughout the body. The pain may be accompanied by tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness, which can worsen over time.
What is the Context of Pain Within Spinal Stenosis?
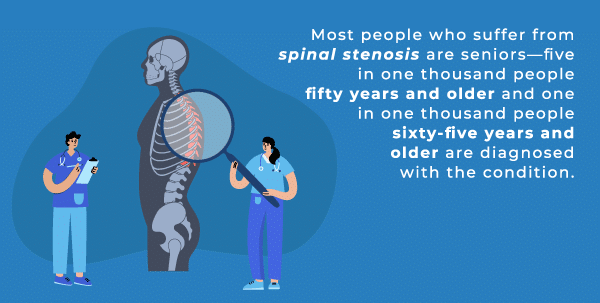
Who Gets Spinal Stenosis?
Spinal stenosis symptoms are most likely to occur in the following individuals:
Seniors
Spinal stenosis is typically brought on by wear and tear on the body. It can also be a side effect of osteoarthritis, herniated discs, and thickened ligaments, which are likely to occur as we age. With that, the condition is more likely to appear in seniors.
People With Paget’s Disease
Paget’s disease is a bone disease that affects adults, causing bone overgrowth in the spine that can lead to spinal stenosis.
People Who Are Prone to Tumors
Tumors can produce spinal stenosis symptoms by forming in the spaces between the spinal cord and vertebrae.
People prone to tumors and those with cancer are at higher risk for developing a narrowing of the spine.
People With Back Injuries
People who have been injured in a car accident or other types of accidents may experience dislocations and fractures in one or more vertebrae.
The displaced bone can damage the spinal canal. Surgery to treat injuries can also put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
Types of Spinal Stenosis
Cervical Stenosis
Cervical stenosis occurs when the spinal canal is too small for the spinal cord and nerve roots. This can cause pinched nerves in the spine and damage the nerve roots and spinal cord.
Cervical stenosis affects the upper part of the back and is characterized by pain in the neck and arms. In advanced stages, it can affect bladder and bowel function and cause pain in the legs and feet.
Lumbar Stenosis
Lumbar stenosis is a narrowing of the spine in the lower back, causing pain in the back and legs. It can affect people’s ability to walk and, like cervical stenosis, it can affect bowel and bladder function.
A Deeper Look Into Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Signs and Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
In the Neck
Neck Pain
Weakness and Clumsiness in the Arm, Hand, Leg, or Foot
The affected nerves may cause pain to radiate throughout the body. Cervical stenosis is more likely to cause pain in the upper body like the hands and arms, while lumbar stenosis affects the lower body like the legs and feet; however, in advanced stages, pain may occur all over.
Problems With Balance
Loss of Function in Hands
Urinary Urges and Incontinence
In advanced stages, spinal stenosis can affect bladder function, leading to urinary urges and incontinence. This is more likely to occur with lumbar stenosis.
In the Lower Back
Pain in the Lower Back
Pain in the lower back is often associated with lumbar stenosis.
Sciatica
It can pinch nerves, causing sciatica—a condition characterized by pain in the back and legs.
Cramping in One or Both Legs
Myelopathy
Loss of Bladder or Bowel Control
Causes of Spinal Stenosis
Bone Overgrowth/Arthritic Spurs
Wear and tear and osteoarthritis can cause bone spurs to form in the spinal canal. These are smooth, hard bumps of extra bone that form at the end of bones. Bone spurs can compress the spine, causing cervical spinal stenosis.
Herniated Discs
Certain Bone Diseases
Achondroplasia
This is the most common form of skeletal dysplasia. Achondroplasia is a birth defect that impairs bone growth in the limbs and causes abnormal growth in the spine and skull.2
Ankylosing Spondylitis
This is an inflammatory disease that causes the bones of the spine to fuse, decreasing flexibility in the spine.
Ankylosing spondylitis may result in a hunched posture and can put pressure on the ribs, making it difficult to breathe.3
Paget’s Disease
Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (OPLL)
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Spinal Injuries
Spinal injuries, such as slipped discs and bone fractures, can cause the vertebrae or bone fragments in the back to put pressure on the nerves in the spine.
Tumors
Arthritis
Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can cause disc space narrowing. Osteoarthritis causes the cushions between the bones to break down and can reduce cartilage between vertebrae, causing bone spurs to grow.
Rheumatoid arthritis causes chronic inflammation that can lead to bone damage and bone spurs.
Thickened Ligaments
Ligaments are the cords that hold the bones of the spine together. They can become stiff and thickened over time, causing a bulge in the spinal cord that can be categorized as back stenosis.
Congenital Spinal Stenosis
Spinal Stenosis Risk Factors
Several risk factors can cause the narrowing of the spine. These include the following:
Degenerative Changes
The bones in the back can degenerate over time; however, the degeneration can speed up if certain conditions are present.
This leads to herniated discs, arthritis, and other issues linked to cervical stenosis symptoms.
Trauma
Trauma can occur due to an accident or surgery. For instance, an incident can cause dislocations and fractures in the vertebrae, and displaced bones can damage the spinal canal.
Scoliosis
Genetic Disease
Various genetic diseases can cause spinal stenosis, such as scoliosis, Paget’s disease, achondroplasia, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Diagnosis and Tests
Patient History
Doctors can determine if patients are at high risk for developing spinal stenosis by reviewing their histories, such as genetic conditions, past traumas, procedures, and general lifestyle activities.
Physical Examination
A medical professional will conduct a physical examination—the patient may be asked to perform a variety of movements to determine the source of back stenosis pain.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
A CT scan may be used for spinal stenosis diagnosis. It involves taking various X-ray images and combining them to provide different angles to make up a cross-sectional image of the affected area.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)- Spine
An MRI uses magnetic and radio waves to provide cross-sectional images of the spine. It can detect ligament and disc damage, tumors, and the source of pressure applied to nerves in the back.
X-Rays
X-rays use radiation to pick up bone spurs and other changes in bone that may be causing the narrowing of the spine.
Myelography

Treatment for Spinal Stenosis
Self-Help Remedies
There are several remedies people can use at home to relieve spinal stenosis symptoms. These include:
Applying Heat
Applying Cold
Exercise
Exercises like flexing, stretching, and strengthening movements may help open up the spine. However, it’s advisable to talk to a physical therapist to determine which exercises are safe before proceeding.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Oral Medications
Oral medications, such as aspirin, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen, can reduce pain and inflammation and are often used in spinal stenosis treatment.
Physical Therapist
Physical therapists teach and recommend exercises that open up the spine. These are performed in their office with the therapist’s assistance, and some exercises can be done at home.
Steroid Injections
Steroid medication (corticosteroid) can be injected into the site of irritation to reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical treatments can be used to eliminate the condition, making them an effective cure for spinal stenosis. They include:
Laminectomy
A laminectomy removes the lamina, or back part, of the affected area to create space around the nerves and relieve the pressure.
In some instances, metal hardware and bone grafts (spinal fusion) may be used to link the vertebrae and maintain spine strength.
Laminotomy
This involves removing only part of the lamina. The procedure is done by carving a hole that’s just large enough to relieve pressure in the affected area.
Laminoplasty
This procedure is recommended for cervical spinal stenosis, as it is performed on the vertebrae in the neck (cervical spine).
Laminoplasty involves creating a hinge on the lamina to make space in the spinal canal. Metal hardware is used to bridge the gap in the open section of the spine.
Foraminotomy
Interspinous Process Spacers
An interspinous spacer can be inserted into the back of the spine. It is placed between spinous processes and gently opened.
Doing so makes space between compressed passages in the vertebra and relieves compression on the nerves.
Spinal Fusion
Spinal fusion is a type of spinal stenosis treatment that connects two or more vertebrae in the back to eliminate motion between them.
It can be used to correct deformities of the spine, such as scoliosis, spinal weakness and instability, and herniated discs, that may be associated with disc space narrowing.
How You Can Prevent Spinal Stenosis
While it’s good to know about the available spinal stenosis treatments, learning about prevention methods can be extremely helpful.
Becoming familiar with how to prevent spinal stenosis can reduce the risk of development, pain, and medical expenses.
Here are some recommended prevention methods:
Eat a Healthy Diet
Don’t Smoke
Nicotine is known to cause cell damage in the annulus and nucleus. This damage can lead to disc degeneration, causing spinal stenosis symptoms.
Avoiding smoking will minimize cell damage and decrease the risk of the condition developing.
Maintain Good Posture
Maintaining good posture will support the natural curves of the back, preventing discs from slipping out of place.
Tips for good posture include learning how to safely lift heavy objects, sleeping on a firm mattress, and practicing posture-improvement exercises, stretches, and positions.
Exercise Regularly
Exercising regularly strengthens the muscles that support the spine and keeps the spine flexible. It also helps the body stay fit.
Overview of Spinal Stenosis
Prognosis and Outlook
The prognosis for spinal stenosis is usually very good, and most people will be able to relieve symptoms with non-surgical treatment effectively.
Nonetheless, in severe stenosis cases, non-surgical treatments will not work as well or be as effective. If this occurs, surgical options may serve as a viable solution.
How J. Flowers Health Institute Can Help
We understand spinal stenosis is not easy to deal with, which is why we provide solutions and treatment options to help you. Our J. Flowers Health Institute team provides high-quality bespoke health care to people of all age groups and offers patients comprehensive care from diagnosis to treatment to aftercare.
With our holistic approach, we focus on both the mental and physical aspects of treatment and recovery to find a solution that works best for each individual. We address a variety of issues, including chronic pain, mental health, and substance use disorders, while providing a comfortable atmosphere that is conducive to healing.
Don’t let spinal stenosis lower your quality of life. Reach out to J. Flowers Health Institute today, and we will get you on a path to healing for a more enjoyable present and future.
Resources
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/myelopathy#:~:text=Myelopathy%20is%20an%20injury%20to,runs%20almost%20its%20entire%20length.
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/achondroplasia#:~:text=Achondroplasia%20is%20the%20most%20common,in%20the%20spine%20and%20skull.
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ankylosing-spondylitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354808#:~:text=Ankylosing%20spondylitis%20is%20an%20inflammatory,be%20difficult%20to%20breathe%20deeply.
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pagets-disease-of-bone/symptoms-causes/syc-20350811
- https://spinehealth.org/the-smoking-spine/#:~:text=In%20time%2C%20improper%20alignment%20and,in%20the%20annulus%20and%20nucleus.
- https://www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Low-Back-Pain
- https://www.medscape.com/answers/1913265-68823/what-is-the-prevalence-of-spinal-stenosis









