
Neurofeedback 101: Understanding the Science of Rewiring Your Brain
This article delves into neurofeedback, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and potential benefits.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Neurofeedback
In today’s fast-paced and competitive world, the pursuit of improved mental health and peak performance has become a priority for many people.
Neurofeedback is a cutting-edge technique that uses brainwave patterns to enhance cognitive abilities and well-being. The approach has emerged as a promising tool in this quest.
Sterman, one of the founders of neurofeedback therapy, trained cats to control their brain waves to handle toxic fumes using rewards. Their brains became ultra-stable and strong enough to withstand fumes. This research aided NASA in developing astronaut training. Presently, NASA still uses biofeedback to teach astronauts to control their sensorimotor rhythms.
Understanding Brain Waves
Before delving into neurofeedback, it is essential to grasp the fundamentals of brainwave patterns and neuroplasticity.
Brain Waves Overview
Here’s a simplified overview of what brain waves are:
“Brain waves are like the electricity in your brain when it’s active. When your brain cells (neurons) talk to each other, they create tiny electrical signals. These signals form different patterns, and we call them brain waves. These brain waves change depending on what you’re doing or feeling, like when you’re relaxed, focused, sleeping, or daydreaming. Scientists use special machines to measure these brain waves and learn more about how our brains work.”1
Brain waves are measured in cycles per second, or hertz (Hz). The different types of brain waves are named after their frequency and can be classified into five categories:2
Delta Waves
These are the slowest brain waves, with a frequency of 0.5-4 Hz. Delta waves are often present during deep sleep and are essential for the restorative functions of:
- Sleep
- Physical healing
- General regeneration
Delta waves are associated with the unconscious mind and play a role in unconscious information processing.
Theta Waves
Theta waves have a 4-8 Hz frequency and are often associated with states of deep relaxation, daydreaming, and light sleep.
They can also occur during:
- Meditation
- Creative thinking
- Vivid imagery
- Accessing deeper levels of consciousness
Theta waves play a crucial role in memory consolidation and learning.
Alpha Waves
These brain wave oscillations occur between the frequency range of 8-12 Hz. They are most prominent when a person is awake but relaxed with closed eyes.
Alpha waves are associated with a calm and meditative mental state. Their presence is often linked to reduced stress and anxiety.
Beta Waves
These are higher-frequency brain waves (12-30 Hz) associated with active and alert mental states such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and active concentration.
Beta waves are present when we are:
- Awake
- Engaged in problem-solving
- Focused on tasks
Beta waves are further divided into low beta (12-15 Hz) and high beta (16-30 Hz) frequencies, with the latter being more associated with heightened alertness and cognitive arousal.
Gamma Waves
Gamma waves have the highest frequency, ranging from 30 to 100 Hertz or higher. They are involved in higher-order cognitive processes, binding sensory information and coordinating various brain regions.
Gamma waves are associated with:
- Peak concentration
- Heightened perception
- Moments of insight or breakthroughs
Almost all patients do not know about their body’s physical and neurological responses until they’re informed.
The Brain's Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity or neural plasticity, refers to the brain’s remarkable ability to change and adapt throughout a person’s life.
- Learning
- Experiences
- Environmental influences
Flexibility and Adaptability
In simpler terms, neuroplasticity is like the brain’s “flexibility” or “adaptability.” It means our brains are not fixed or unchangeable; they can continuously form new connections between neurons and reshape existing ones.
This process allows the brain to:
- Learn from experiences
- Recover from injuries
- Adjust to various situations
Examples of Neuroplasticity
For example, when we learn something new, like playing a musical instrument or a new language, our brain forms new connections between neurons to store that information.
Similarly, if a part of the brain gets damaged due to injury or stroke, neuroplasticity enables it to reorganize itself and reassign functions to other areas to compensate for the loss.
Importance of Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain injuries.
It has significant implications for:
- Rehabilitation therapies
- Education
- Understanding of various brain-related conditions and their treatments
The brain’s ability to change and adapt through neuroplasticity allows us to continually learn, grow, and adapt throughout our lives.
Types of Neuroplasticity
There are two main types of neuroplasticity:
Functional Plasticity: This refers to the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize its functions to compensate for injury or learn new skills.
Structural Plasticity: The brain’s ability to physically change its structure by forming new connections between neurons or modifying existing ones in response to experiences and learning.
The Benefits of Brain Training
Understanding Neurofeedback
For example, the user might see a bar graph that goes up when producing the desired brain wave pattern or hear a tone that gets louder when they are doing the right thing.
Benefits of Neurofeedback
With this feedback, people can learn to control their brain waves and improve their brain’s performance, which may help reduce stress, improve focus, or manage emotions.
Neurofeedback takes advantage of neuroplasticity (the brain’s ability to change) and helps people improve their brainwave patterns, leading to:
- Better mental health
- Increased cognitive abilities
- Helping the brain recover from challenges or injuries
Types of Neurofeedback Systems
Many different types of neurofeedback systems are available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common types of neurofeedback systems include:
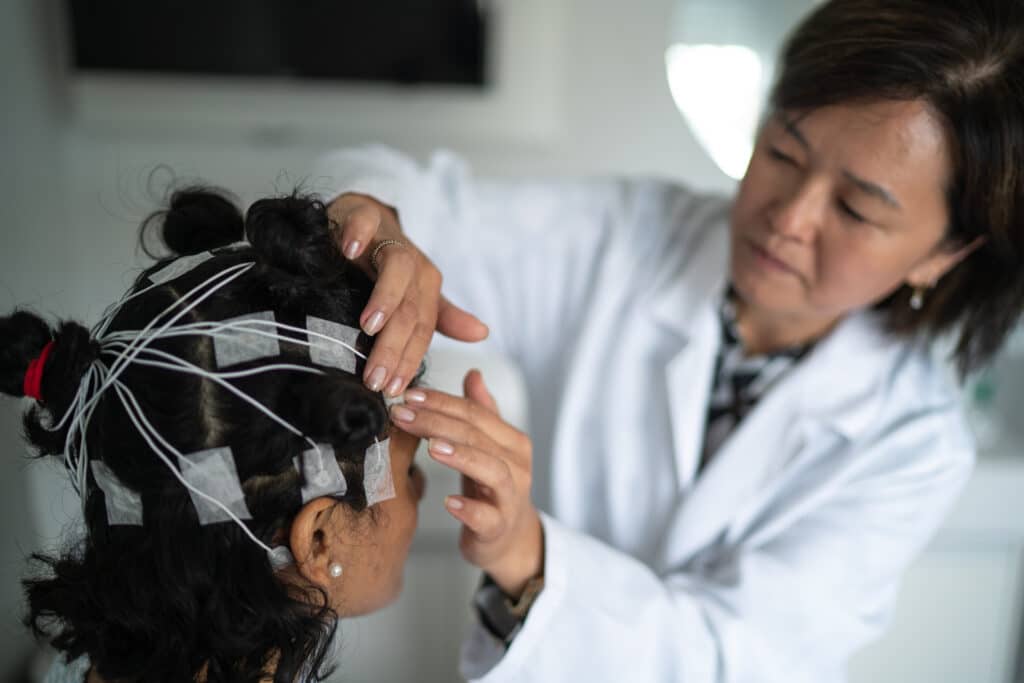
EEG Neurofeedback
EEG neurofeedback is the most common type of neurofeedback. It uses electroencephalography (EEG) to measure brain waves.
EEG is a non-invasive procedure that involves placing electrodes on the scalp. The electrodes detect the brain’s electrical activity and transmit this information to a computer. The computer then analyzes the EEG data and provides real-time feedback to the user.
qEEG Neurofeedback
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Neurofeedback
fMRI neurofeedback relies on functional magnetic resonance imaging technology to measure brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow. It provides a more localized view of brain activity than EEG. But, it’s less often used due to the high cost and limited availability of fMRI machines.
Hemoencephalography (HEG) Neurofeedback
HEG neurofeedback measures changes in blood oxygenation in specific brain regions, providing feedback on blood flow levels.
It’s often used in neurofeedback protocols targeting the prefrontal cortex to enhance:
- Focus
- Attention
- Emotional regulation
Each system has unique benefits and applications, but EEG neurofeedback is the most widely used due to its accessibility and effectiveness.
The Benefits of Brain Training
What is Neurofeedback Therapy?
Goals of Neurofeedback Therapy
The person’s goal during neurofeedback therapy is to learn how to self-regulate their brain activity by receiving this real-time feedback.
For example, they may be shown a video game or a movie, and their brain’s activity will influence the game or movie’s speed or volume. As they practice and receive feedback, they gradually learn to control their brainwave patterns consciously.
After neurofeedback therapy, patients who took the MMPI-2 personality test showed significant improvement in five out of its ten scales.
Applications of Neurofeedback Therapy
Neurofeedback aims to improve brain functioning, emotional well-being, and cognitive performance by promoting self-awareness and self-regulation.
It takes advantage of the brain’s neuroplasticity, enabling it to rewire and adapt in response to training, potentially improving mental health and cognitive abilities.
Neurofeedback therapy is used to address various conditions, including:
ADHD
Research on neurofeedback as a treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has shown promising results.
Some studies indicate that neurofeedback training, particularly targeting beta and theta wave ratios, can improve:
- Attention
- Impulse control
- Hyperactivity in children and adults with ADHD
Anxiety and Depression
Neurofeedback has been explored as a potential adjunctive therapy for anxiety and depression. By encouraging brainwave patterns associated with relaxation and positive emotional states, neurofeedback may help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression and improve overall mood.
Cognitive Enhancement
Neurofeedback has also been studied in the context of cognitive enhancement.
By training brainwave patterns linked to attention, memory, and cognitive focus, neurofeedback may offer benefits in academic and professional settings, potentially enhancing learning and cognitive performance.
Complementary Therapy
Neurofeedback is often used as complementary therapy in conjunction with conventional medical and psychological treatments. It is not a standalone treatment but a supportive intervention that can enhance treatment outcomes.
Neurofeedback may help people cope with various conditions and improve their quality of life by promoting self-regulation of brainwave patterns.
Stress and Sleep Disorders
Neurofeedback has shown promise in managing stress and anxiety by encouraging relaxation-promoting brainwave patterns, such as alpha and theta waves.
For sleep disorders, neurofeedback can target brainwave patterns associated with improved sleep quality and reduced insomnia symptoms.
Trauma and PTSD Treatment
In the context of trauma and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), neurofeedback can get used to address symptoms related to:
- Emotional dysregulation
- Hyperarousal
- Intrusive memories
Neurofeedback may help people cope with traumatic experiences and improve emotional resilience by training brainwave patterns associated with emotional stability and cognitive control.
Substance Use Disorder and Addiction
Neurofeedback has been explored as a potential adjunctive therapy for substance use disorder and addiction.
By targeting brainwave patterns linked to impulse control, emotional regulation, and decision-making, neurofeedback may aid people in managing cravings and developing healthier coping mechanisms during addiction recovery.
Pain Management
Chronic pain can be challenging to treat, and neurofeedback has been investigated as a non-pharmacological approach to pain management.
Neurofeedback may help people modulate their pain perception and reduce the emotional distress often associated with chronic pain conditions by training brainwave patterns associated with relaxation and pain relief.
Seizures
Medical treatment is often ineffective in patients with diagnosed epilepsy. Neurofeedback training focused on specific brain waves has proven effective in improving symptoms.
Some studies show that neurofeedback reduces the rate of seizures in people with severe and uncontrolled epilepsy.
Autism Spectrum Disorders
Neurofeedback is being studied as a potential intervention for people with autism spectrum disorders (ASD).
The goal is to target brainwave patterns that may contribute to improved:
- Social communication
- Cognitive flexibility
- Emotional regulation in people with ASD
While research is still ongoing, early findings suggest some potential benefits.
Brain Training in ASD
Improving Attention and Focus
Neurofeedback can enhance attention and focus by training people to regulate brainwave patterns associated with sustained attention.
For example, increasing beta wave activity in specific brain regions linked to focus and concentration may improve a person’s ability to stay on task and avoid distractions.
Enhancing Memory and Learning Abilities
Neurofeedback has been explored as a potential tool for improving memory and learning abilities. By targeting brainwave patterns related to memory consolidation, such as theta waves during deep sleep, people may experience enhanced memory retention and learning outcomes.
Sports Performance
Athletes often seek ways to optimize their performance, and neurofeedback is being explored as a potential tool in sports psychology.
By training brainwave patterns associated with the “flow” state (a mental state of full immersion and peak performance), athletes may achieve:
- Better focus
- Improved coordination
- Optimal performance during competitions
Artistic and Musical Abilities
For musicians and artists, achieving a state of enhanced creativity and artistic flow is crucial. Neurofeedback protocols targeting brainwave patterns related to creativity and enhanced focus may aid artists and musicians in unlocking their full creative potential.
Other Conditions
Neurofeedback has also proven successful in treating symptoms of:
- Schizophrenia
- Learning disabilities
- Relieving chronic pain
- Stroke recovery
- Eating disorders
- Parkinson’s disease
- Fibromyalgia
- Restless leg syndrome
- Many others
Many people report feeling more confident after discovering they can control their reactions to physical stress.
Neurofeedback for Children
Neurofeedback is a non-invasive process that does not take medications or other physical interventions. The non-invasive nature of neurofeedback makes it an excellent way to address various mental health conditions and conditions of the brain in children.
What it Treats in Children
Neurofeedback has proven beneficial in addressing:
- Teeth grinding
- Sleep problems
- Nightmares
- Bedwetting
Using the same neurofeedback processes used for adults with sleeping difficulties, neurofeedback therapists can help calm the overactive areas of the brain that lead to many nighttime complications experienced by younger children.
Neurofeedback Safety and Efficacy
Neurofeedback is often considered a safe and non-invasive technique. When conducted by trained professionals and following established protocols, adverse effects are rare.
But, it’s essential to consider the following safety and efficacy considerations:
Professional Qualifications
Neurofeedback should be administered by qualified and certified practitioners who have undergone appropriate training and have a thorough understanding of neurofeedback protocols and practices.
Individualized Treatment
Neurofeedback protocols should get tailored to each person’s unique needs and conditions. One-size-fits-all approaches may not be as effective as personalized treatment plans.
Monitoring and Supervision
The neurofeedback process should be closely monitored and supervised by practitioners to ensure safety and track progress.
Potential Side Effects
While uncommon, some people may experience mild side effects during or after neurofeedback sessions, such as temporary fatigue or headache. These effects are often short-lived and resolve on their own.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical practices, confidentiality, and informed consent are vital in administering neurofeedback.
The Promising Future of Neurofeedback
The future of neurofeedback is bright and holds many possibilities for advancement. As technology evolves, we can expect:
- More sophisticated brainwave monitoring equipment
- Improved feedback systems
- Increased accessibility through wearable devices and mobile applications
Neurofeedback’s integration into mainstream healthcare and education settings has the potential to transform the way we approach mental health, cognitive enhancement, and brain rehabilitation. As research continues, we may unlock even more potential benefits and applications of neurofeedback.
The Process of Neurofeedback
To get the most out of a neurofeedback session, being comfortable with the process is essential. Remember to ask your provider any questions about the process and be open about your concerns at all points during your first appointment.
What to Do Before a Session
If you take any medications, continue to do so unless directed otherwise. Do not stop taking any prescription medications without contacting your provider, as suddenly stopping certain medications can be dangerous.
Drink plenty of water before and after your session. Consider bringing a driver to your appointment. Sometimes, patients feel tired after their session and may not feel comfortable driving.
Brain Mapping
The first step in neurofeedback treatment is to create a brain map using quantitative EEG or qEEG. This process helps your neurofeedback therapist identify what brain areas are damaged or not working as they should.
Once this vital information has been collected, your therapist can tailor your neurofeedback training to meet your specific treatment needs and goals.

Discover the Optimal Neurofeedback Center in Houston, Texas
When it comes to neurofeedback therapy, finding the right center can make all the difference in your journey toward improved well-being.
At J. Flowers Health Institute, we understand the significance of a well-suited neurofeedback program. We offer a diverse range of specialized treatments to cater to individual needs.
Our team of skilled and highly trained, world-class experts is dedicated to guiding you on a path of healing that encompasses your body, mind, and spirit.
Our Process
We begin by conducting a comprehensive evaluation and diagnostic review of your symptoms, enabling us to understand the areas that may benefit from neurofeedback therapy.
This personalized approach ensures that we address the root causes of your concerns and help you achieve the healthiest and most holistic version of yourself.
Our Treatment Environment
Located in a luxurious private treatment center, we create a supportive and nurturing environment where you can focus on your recovery.
Our neurofeedback programs are designed to address various conditions, including:
- Addiction
- Behavioral concerns
- Issues stemming from traumatic brain injuries
By combining cutting-edge neurofeedback techniques with compassionate care, we aim to help you overcome physical, mental, and behavioral struggles, leading you toward personal growth and transformation.
Contact J. Flowers Health Institute Today
If you or a loved one could benefit from neurofeedback therapy, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at J. Flowers Health Institute. We are committed to giving you the happy, healthy, and fulfilling life you deserve.
Our team is committed to providing you with the highest level of care and support on your journey to improved well-being and a better quality of life.
Contact us today to learn more about the benefits of neurofeedback therapy and how it can positively impact your life.
Resources
- https://www.diygenius.com/the-5-types-of-brain-waves/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4892319/
- https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-brain-plasticity-2794886
- https://www.eeginfo.com/what-is-neurofeedback.jsp
- https://qeegsupport.com/what-is-qeeg-or-brain-mapping/
- https://www.verywellmind.com/neurofeedback-therapy-definition-techniques-and-efficacy-5193195
- https://www.forbes.com/health/mind/what-is-neurofeedback-therapy/









