
What is AMPS?
Some may question, what is Amplified Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome? AMPS is a medical condition causing intense pain to those who have it.
Table of Contents
What is Amplified Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome (AMPS)?
The cause of amplified musculoskeletal pain syndrome is not well understood, but current research suggests it stems from an overreaction of the pain signals by the central nervous system. While AMPS can affect anyone, it is seen mostly in children. Around 80% of people with AMPS are pre-adolescent and adolescent girls.2
Musculoskeletal Pain Causes and Risk Factors
So, what causes amplified musculoskeletal pain? Typically, AMPS is triggered by an injury or an illness, like a broken bone. It may also be triggered by psychological stress, mental illness, or emotional trauma. With this condition, there is a “short-circuit” in the pain response, which causes a person’s typical reaction to pain to change. Typically, when someone without AMPS experiences pain, the sensation travels from the site of the injury to the spinal cord, then to the brain.
Causes of Musculoskeletal Pain Overview
Risk Factors
- Age: Younger people are more likely to experience this disorder.
- Gender: The condition is more common in females.
- Genetics: Genetics can be an underlying genetic susceptibility that is triggered by stress, illness, or injury.
- Family History: People with a family member with a pain disorder are more likely to also have a pain disorder.
- Illness: Illness can trigger the onset of musculoskeletal pain.
- Injury: Musculoskeletal pain or injury can trigger AMPS.
- Stress: Stress can trigger the onset of AMPS.
High-Risk Musculoskeletal Pain Conditions
AMPS is often seen in children, and some researchers suggest that it is triggered by joint flexibility and “growing pains.” People with AMPS often have more flexible joints than the average person and have a history of experiencing muscle and joint pain.
Those who have experienced emotional trauma or psychiatric conditions may also be more susceptible to AMPS. Additionally, some conditions that may put you at higher risk for musculoskeletal pain will be detailed below.
Arthritis
Fibromyalgia
Tunnel Syndromes
Tunnel syndromes, like carpal tunnel, cause tingling, numbness, and pain in affected areas. Carpal tunnel happens when one of the major nerves in the hand becomes compressed as it travels to the wrist. AMPS may be more common in people with tunnel syndromes.
Signs and Symptoms of Musculoskeletal Pain

Allodynia
Allodynia Overview
Changes to the Skin
Problems with Movement
AMPS can affect a person’s ability to move and function normally. This may mean that the individual cannot stand for long periods, lift heavy objects, or even tolerate touch, depending on the location(s) and severity of the pain.
- Edema or swelling
- Changes to hair in the affected area
- Headaches
- Dizziness
AMPS and Mental Health
Anyone living with a chronic pain condition can attest to the fact that feeling pain on a constant basis can have a tremendous impact on a person’s quality of life.
Studies show that people who experience chronic pain have a significantly lower quality of life due to pain inhibiting them from functioning normally and participating in the activities they would like to do.6
Can AMPS Be Mentally Draining?
AMPS, like other chronic pain conditions, can not only be physically painful but also mentally draining. People with amplified musculoskeletal pain syndromes may be more likely to experience anxiety, depression, brain fog, and other mental health concerns.
Also, it is important to note that stress can be one of the causes of AMPS, so it’s important to manage stress levels as much as possible.
How is Musculoskeletal Pain Diagnosed?
Initial Evaluation
In the initial examination, your doctor will talk with you about the pain you are experiencing and any other signs or symptoms you may have.
Since AMPS can be hard to diagnose, doctors must look at a patient’s complete medical history and ask many questions in the initial exams.
- How long have you been experiencing pain?
- In which areas of the body do you feel pain or other symptoms?
- Is the pain constant, or does it come and go?
- What is the pain level?
- How are you currently managing the pain?
- What makes it worse or better?
- What does the pain feel like (stabbing, sharp, dull, etc.)
Physical Examination
Testing
Lab Tests
X-rays
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Computed Tomography (CT)
Joint Fluid Testing

Preventing and Living with Amplified Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome (AMPS)
- Be sure to warm up before exercising to avoid putting too much stress on the body.
- Stretch before workouts and between long bouts of sitting or staying in the same position. Take breaks from any constant posture every 20 minutes and pay attention to any muscles that begin to become stiff.
- Listen to your body. If an activity is painful, be sure to stop the activity.
- Tend to an injury earlier rather than later.
Posture Tips
- Keep the back straight, and the shoulders relaxed. Be careful with twisting and bending motions.
- Set up your workspace so that your body is directly in front of your work and doesn’t require you to stretch or strain.
- Keep wrists as neutral as possible; the wrists should not be extended further than 15 degrees in any direction.
- Most of us don’t realize how much time we spend bending our necks forward to look at computers or smartphones. However, it’s important to avoid doing this, as it can lead to neck injuries.
- Avoid sitting or standing in the same position for an extended period. Muscles tire more quickly when they are held in the same position. Try to take frequent breaks and increase blood circulation.
Posture Tips
Coping with Musculoskeletal Pain
Aside from medical treatments for AMPS, which we will explain below, there are other ways to cope with musculoskeletal pain. Adapting your lifestyle and everyday actions to support your healing and minimize pain and stress is important. Some things you can do at home to help maintain well-being while dealing with AMPS include:
Minimize Stress
Don’t take on more work than you can handle. It can be hard to say no to additional tasks or work projects if you’re used to working a lot, but putting too much on your plate is likely to raise your stress levels.
Additionally, take steps to avoid other sources of stress in your life, whether it’s certain people or situations that stress you out.
Try Yoga or Meditation
Studies show that exercise is good for the body, but yoga may provide increased stress relief due to its meditative elements.
Experiencing the pain of AMPS may negatively impact one’s quality of life, but research shows that yoga can significantly improve the quality of life, making yoga a great option for people with musculoskeletal pain.8
Make Time For Joy

Treatment for AMPS Amplified Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome
Treatment for AMPS amplified musculoskeletal pain syndrome will vary based on an individual’s circumstances, but musculoskeletal pain treatment typically involves the following interventions:
Medication
Musculoskeletal pain medication is often a first line of defense against AMPS in adults; however, it is not always a first choice for children with the condition.
Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, aspirin, or naproxen are often used to manage pain. In some severe cases, opioids may be prescribed.
Therapy
For adults and children, therapy can be a useful treatment for AMPS. Physical therapy can help individuals tone muscles and improve symptoms.
Psychotherapy is also useful, as it can teach individuals how to cope with the stress that comes along with AMPS and can help them learn how to function even while experiencing pain.
Aids and Devices
Surgery
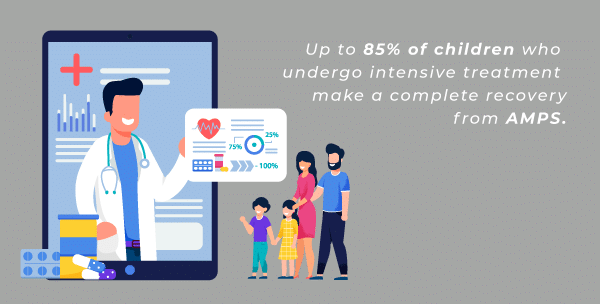
As you complete treatment for AMPS, you can expect to experience fewer musculoskeletal pain symptoms each day. Treatment for AMPS typically leads to a gradual recovery which, in children, can be shown by improved school attendance and activity participation.
For amplified musculoskeletal pain syndrome in adults, recovery can be more easily measured and discussed with a musculoskeletal pain doctor.
Treatment at J. Flowers Health Institute
At J. Flowers Health Institute, you can receive treatment for AMPS and other musculoskeletal pain disorders, bringing you relief from symptoms and a more positive outlook. Reach out today to learn more.
Resources
- https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/amplified-musculoskeletal-pain-syndrome-amps
- https://www.columbiadoctors.org/childrens-health/pediatric-specialties/rheumatology/treatments-conditions/amplified-musculoskeletal-pain-syndrome-amps
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17933-amplified-musculoskeletal-pain-syndrome-amps-in-children
- https://www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Patient-Caregiver/Diseases-Conditions/Amplified-Musculoskeletal-Pain-Syndrome-AMPS
- https://whyy.org/segments/for-these-teens-the-only-way-to-overcome-pain-is-to-face-it/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31218259/
- https://www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Patient-Caregiver/Diseases-Conditions/Amplified-Musculoskeletal-Pain-Syndrome-AMPS
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3193654/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/magazine/happiness-stress-heart-disease/






